In today’s fast-paced world, a sedentary lifestyle has become a silent epidemic affecting millions worldwide. The impact of prolonged inactivity on health and well-being is increasingly concerning to scientists and healthcare experts. But what exactly is a sedentary lifestyle, and why should we be worried about its consequences?

(image: getty image)
What is a Sedentary Lifestyle?
A sedentary lifestyle refers to a way of living that involves minimal physical activity. It often includes extended periods of sitting or lying down, such as working on a computer, watching television, or spending hours on a mobile device. Daily physical activities like walking or even standing are significantly reduced, leading to long-term health risks.
Causes of a Sedentary Lifestyle
Several factors contribute to this inactive way of life. Here are some key reasons:
- Technological Advancements: With the rise of computers, smartphones, and digital entertainment, people are more likely to remain seated for prolonged periods. From remote work to binge-watching TV shows, technology has undeniably transformed daily routines.
- Cultural Values: In many societies, especially in highly developed nations, productivity often outweighs physical movement. Sitting for hours at a desk is seen as a symbol of dedication and success, indirectly promoting a sedentary routine.
- Urbanization: As cities expand, people become more reliant on cars and public transport. Walkable communities are diminishing, leading to fewer opportunities for physical activities in daily life.
Consequences of a Sedentary Lifestyle
Prolonged inactivity can have severe health consequences. Here’s a breakdown of the major risks:
- Obesity or Morbid Obesity: Inactivity reduces the body’s ability to burn calories, leading to weight gain. Over time, this can progress to obesity, increasing the risk of other chronic conditions.

(image: getty image)
- Reduced Lipoprotein Lipase Activity: Physical inactivity decreases the activity of lipoprotein lipase, an enzyme that helps break down harmful triglycerides. This can lead to higher levels of “bad” fats in the blood.
(image: getty image)
- Increased Risk of Hypertension: Extended periods of inactivity are linked to higher blood pressure, which can have severe implications for cardiovascular health.

(image: getty image)
- Greater Risk of Depression and Anxiety: Studies show a clear connection between sedentary behavior and mental health issues, such as anxiety and depression. Lack of physical activity can affect brain chemistry, which plays a significant role in mood regulation.
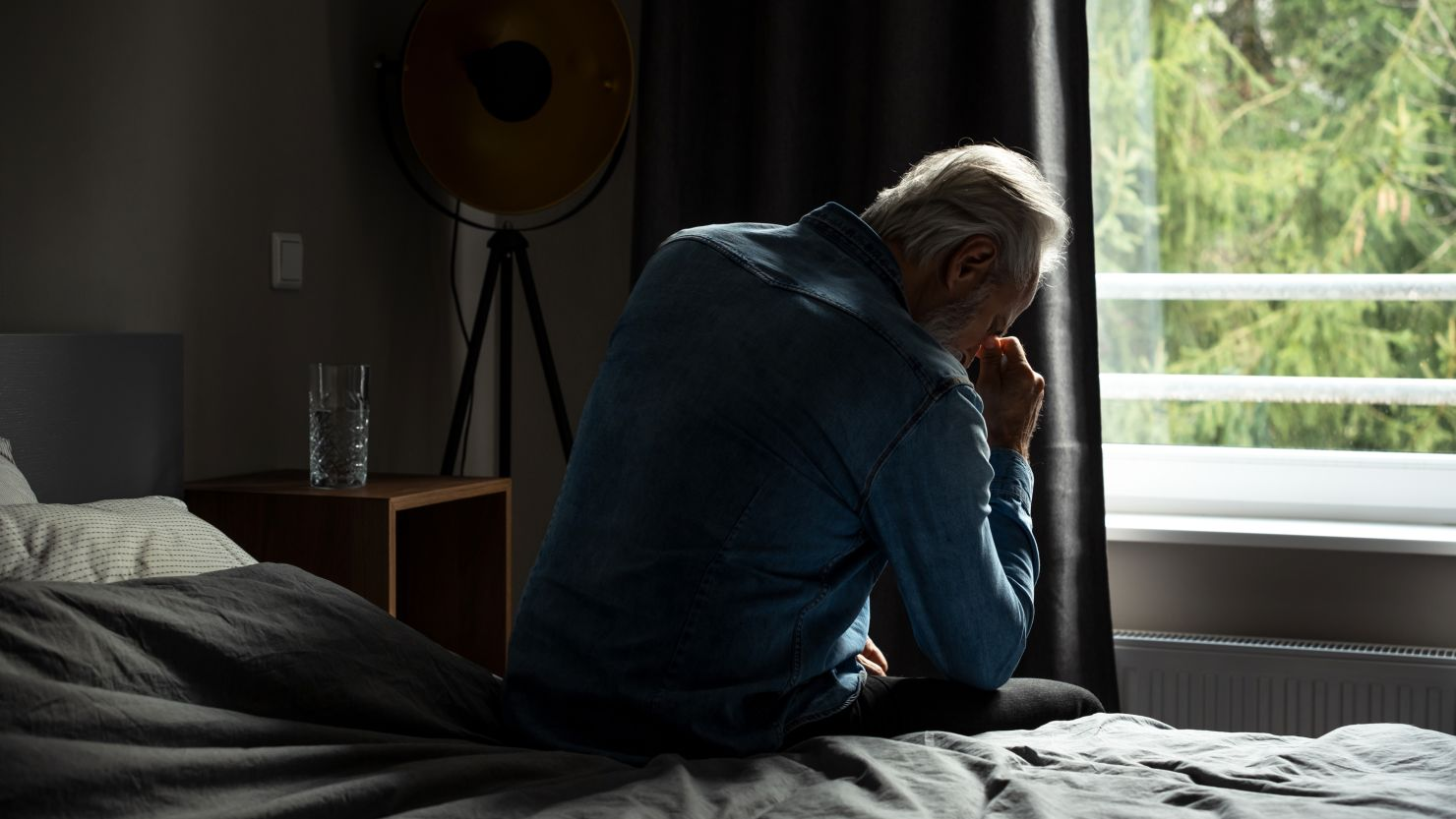

(image: getty image)
- Higher Risk of Stroke: Being inactive significantly increases the risk of suffering from a stroke, one of the leading causes of death worldwide.

(image: getty image)
- Decreased Skeletal Muscle Mass: A sedentary lifestyle leads to muscle atrophy over time, causing a decline in physical strength and endurance.
(image: getty image)
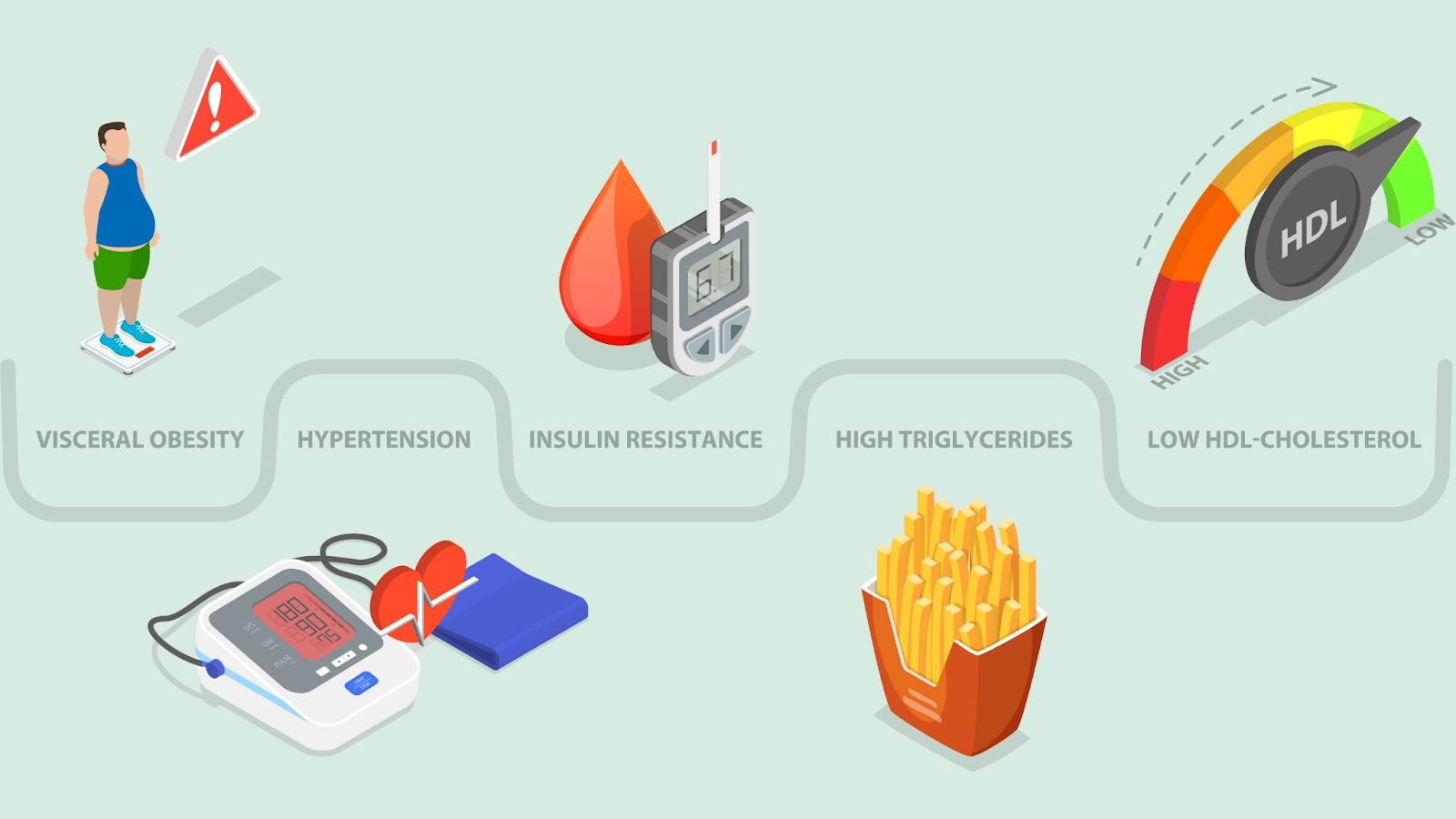
- Elevated Risk of Metabolic Syndrome: A cluster of conditions like high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, metabolic syndrome, is a direct outcome of inactivity.
(image: getty image)
- Higher Risk of Falls in Older Adults: Sedentary behavior can lead to reduced muscle strength and balance, increasing the likelihood of falls in elderly individuals.
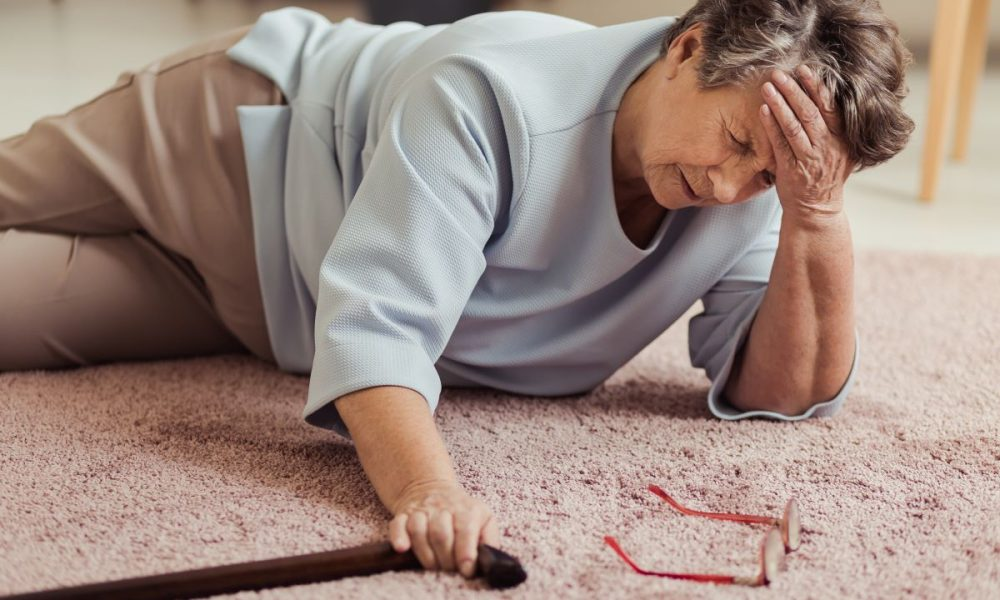

(image: getty image)
Severe Health Implications:
- Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Mortality: Extended inactivity raises the risk of developing heart diseases, which remain the leading cause of death globally.
- Higher Cancer Risks: Sedentary behavior has been linked to an elevated risk of certain cancers, including colon and breast cancer.
- Greater Chance of Type 2 Diabetes: Long-term inactivity negatively impacts insulin sensitivity, increasing the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Higher Risk of Osteoporosis: Reduced weight-bearing activities weaken bone density over time, making bones more susceptible to fractures and osteoporosis.
Solutions to Combat a Sedentary Lifestyle
Combating a sedentary lifestyle is essential for long-term health and well-being. Here are some practical solutions:
- Incorporate Movement into Your Routine: Take regular breaks from sitting, even if it’s just to stretch or walk for a few minutes. Simple practices like taking the stairs or parking farther away can make a big difference.
- Adopt Physical Hobbies: Engage in activities like gardening, walking your dog, or taking up a sport. Finding enjoyable activities can encourage consistent movement.
- Ergonomic Workspaces: Invest in a standing desk or ergonomic chair to encourage better posture and more frequent movement while working.
- Set Realistic Goals: Start small by incorporating short exercise routines, gradually increasing the intensity and duration as you build endurance.
- Monitor Your Activity: Use fitness trackers or mobile apps to set reminders to move regularly. Tracking steps and activities can boost motivation and consistency.

(image: getty image)
By understanding the consequences of a sedentary lifestyle and taking proactive measures, you can improve your quality of life and avoid serious health risks. Stay tuned for more lifestyle tips, and remember to follow our page for regular updates on health, wellness, and fitness!


